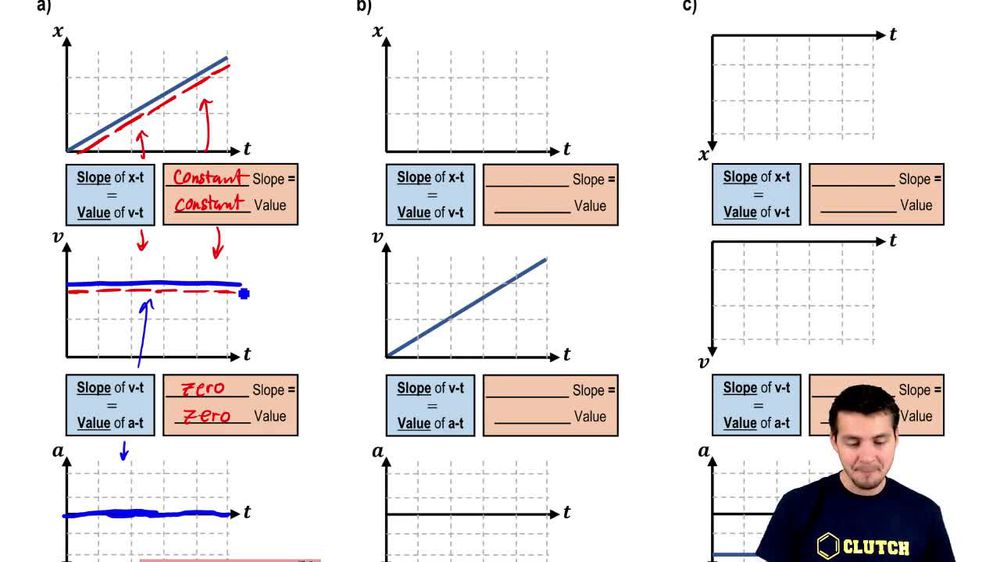
Constant Velocity In A Graph . Recall that velocity is defined as. the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew in the last snap lab to create a velocity graph. therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t) is a straight line, and the slope of the. If the rolling ball slowed down. a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c). in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the.
from www.pearson.com
a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t) is a straight line, and the slope of the. the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c). If the rolling ball slowed down. in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew in the last snap lab to create a velocity graph. Recall that velocity is defined as. in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the.
Interpreting Motion Graphs Pearson+ Channels
Constant Velocity In A Graph the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c). Recall that velocity is defined as. the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the. therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t) is a straight line, and the slope of the. in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew in the last snap lab to create a velocity graph. If the rolling ball slowed down. a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant.
From www.teachoo.com
Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts Constant Velocity In A Graph As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c). a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. If the rolling ball slowed down. Recall that velocity is defined as. in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From wiringvigono7zpqw.z22.web.core.windows.net
Motion Diagram Of A Car Moving At A Constant Velocity Constant Velocity In A Graph the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. Recall that velocity is defined as. As. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Graphical Analysis Of Motion PowerPoint Presentation ID296566 Constant Velocity In A Graph As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c). If the rolling ball slowed down. in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew in the last snap lab to create a velocity graph. Recall that velocity is defined as. therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t). Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.youtube.com
Motion Graphs (1 of 8) Position vs. Time Graph Part 1, Constant Constant Velocity In A Graph a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c). the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From sites.google.com
Unit 2 MotionSpeed and Acceleration Michael Jones 4A Physics Constant Velocity In A Graph Recall that velocity is defined as. If the rolling ball slowed down. a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t) is a straight line,. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Motion with Constant Velocity in 1D PowerPoint Presentation, free Constant Velocity In A Graph As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c). If the rolling ball slowed down. Recall that velocity is defined as. the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew in. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From the-physics-city.blogspot.com
Physics Constant Velocity Constant Velocity In A Graph therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t) is a straight line, and the slope of the. in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the. If the rolling ball slowed down. in. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Motion with Constant Velocity in 1D PowerPoint Presentation, free Constant Velocity In A Graph a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. If the rolling ball slowed down. in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the. As. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From namastesensei.in
Velocity Time Graph For Uniform Motion With Example Constant Velocity In A Graph in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the. If the rolling ball slowed down. a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. . Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From theodore-has-rowland.blogspot.com
B Draw a Graph of the Velocity Function TheodorehasRowland Constant Velocity In A Graph therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t) is a straight line, and the slope of the. the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.teachoo.com
Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts Constant Velocity In A Graph therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t) is a straight line, and the slope of the. If the rolling ball slowed down. in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew in the last snap lab to create a velocity graph. a body moves with uniform. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.youtube.com
Constant Velocity Distance Time graph YouTube Constant Velocity In A Graph the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. If the rolling ball slowed down. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c). in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.ausgas.co
constant velocity motion constant velocity transmission Aep22 Constant Velocity In A Graph the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. therefore, for linear motion with constant velocity, the graph of position vs time (x vs t) is a straight line, and the slope of the. If the rolling ball slowed down. Recall that. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.pearson.com
Interpreting Motion Graphs Pearson+ Channels Constant Velocity In A Graph Recall that velocity is defined as. a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew in the last snap lab to create a velocity graph. the velocity of a. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.youtube.com
Motion Graphs (4 of 8) Velocity vs. Time Graph Part 1 YouTube Constant Velocity In A Graph in this lab, students will use the displacement graph they drew in the last snap lab to create a velocity graph. in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the. If the rolling ball slowed down. therefore, for linear motion with. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.youtube.com
Constant Velocity Graph YouTube Constant Velocity In A Graph a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the. the velocity of a particle is. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From study.com
Constant Velocity Definition, Equation & Graph Lesson Constant Velocity In A Graph If the rolling ball slowed down. in the middle section of the position versus time graph where the slope is constant we see that we have a constant velocity on the. Recall that velocity is defined as. the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does. Constant Velocity In A Graph.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Interpreting Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Constant Velocity In A Graph Recall that velocity is defined as. a body moves with uniform rectilinear motion (u.r.m.) when it has constant velocity, i.e., when its trajectory is a straight line and its speed is constant. the velocity of a particle is constant if an object is moving equal distances at equal intervals of time and does not change its direction. . Constant Velocity In A Graph.